Dr. Ravi Nagar
Menu
Emergency? Call us!
+91 7869966988
+91 7869966988
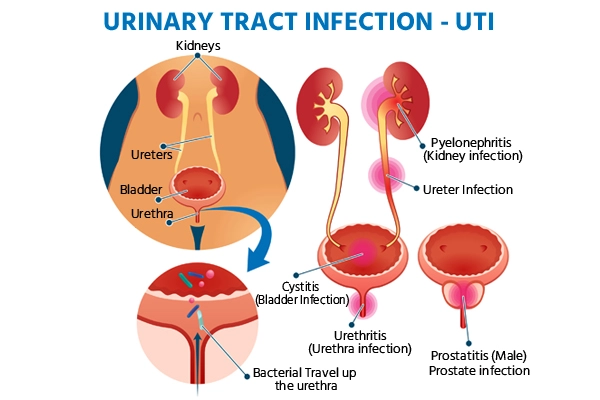
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections that occur when bacteria invade and multiply in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. UTIs can cause a range of symptoms and may vary in severity, from mild discomfort to serious complications.
Description: An infection of the bladder. It is the most common type of UTI. Symptoms: Frequent and painful urination, lower abdominal discomfort, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. It may also cause blood in the urine (hematuria).
- **Description**: An infection of the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body. - **Symptoms**: Painful urination, a burning sensation during urination, and discharge from the urethra.
- **Description**: An infection of one or both kidneys, which can be more severe than other types of UTIs. - **Symptoms**: High fever, chills, flank pain (pain in the side or back), nausea, and vomiting. Pyelonephritis often results from a bladder infection that has spread to the kidneys.
- **Description**: An infection of the ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. It is less common but can occur in conjunction with other UTIs. - **Symptoms**: Similar to cystitis and pyelonephritis, including pain during urination and lower abdominal discomfort.
UTIs are primarily caused by bacteria, most commonly *Escherichia coli* (E. coli), which normally inhabit the digestive tract. Factors that increase the risk of developing a UTI include female anatomy, sexual activity, urinary tract abnormalities, a suppressed immune system, and use of certain medications.
Diagnosis typically involves urine tests to detect the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, and other indicators of infection. Imaging studies may be used in more complex cases. Treatment usually involves antibiotics to eliminate the infection, with the choice of medication based on the type of bacteria and the patient's overall health. Drinking plenty of fluids and practicing good hygiene can help prevent UTIs.
Understanding the different types of UTIs and their symptoms is important for effective diagnosis and treatment, ensuring prompt relief and reducing the risk of complications.